Physical computing is the act of making machines react to people
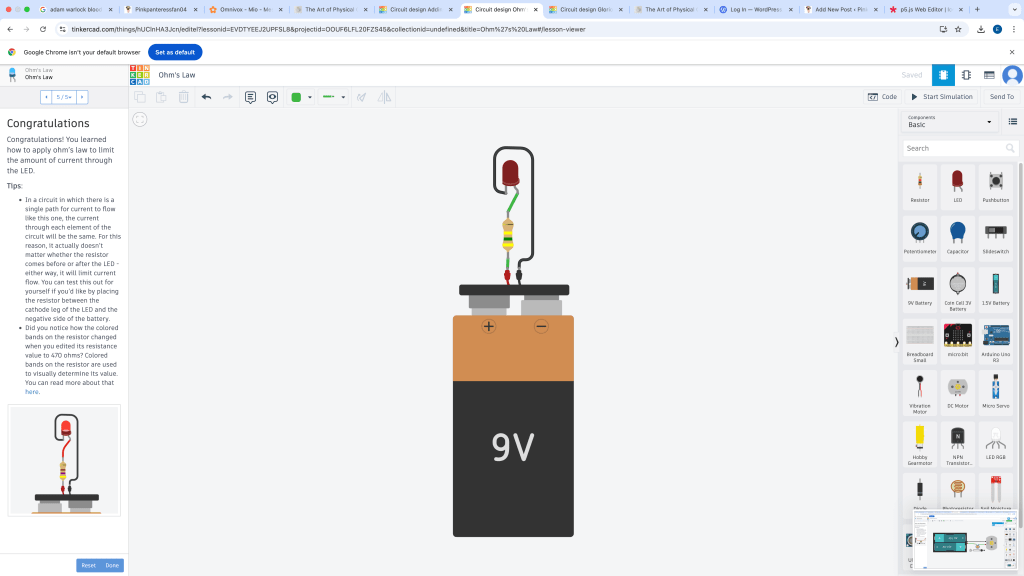
Ohm’s Law
Voltage(V)= Current(I) * Resistance(R)

Types of resistors
Resistors “resist” how many electrons flow through a current
-Carbon composite resistors
-Carbon film resistors(Most common)
-Metal film resistors
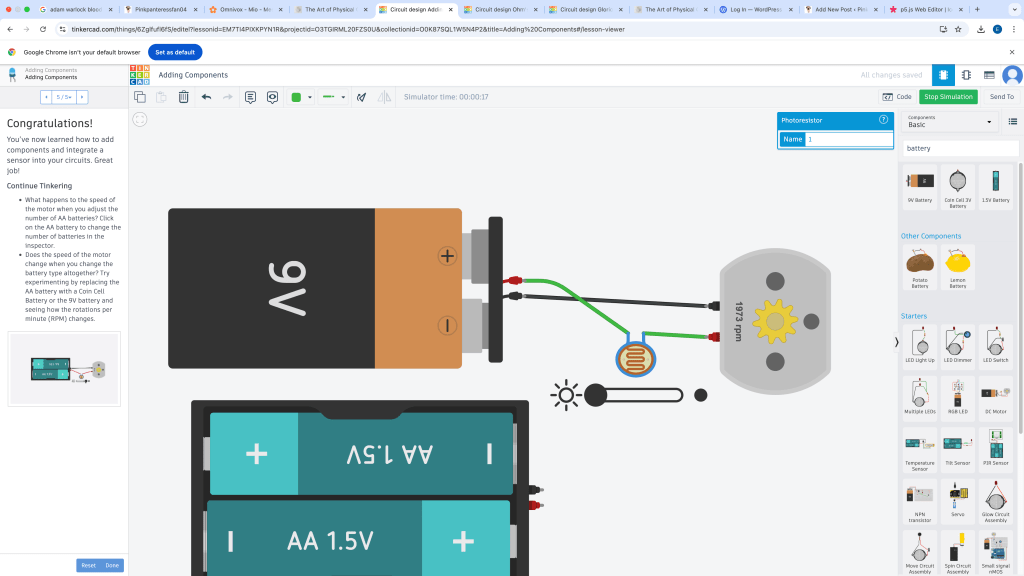
Variable resistors
-PhotoCell- Not polarized (Can go either way)
-Rheostat
-Force sensitive
-Thermostor Resistor
-Slide Potentiometer

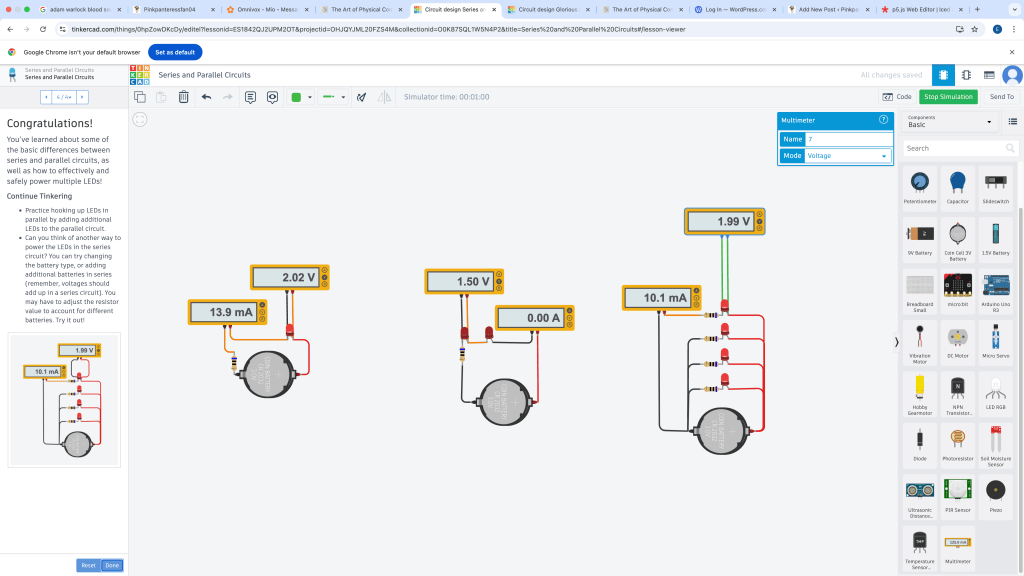
Series circuits- In this circuit there are no branches and thus we have the same current everywhere
Parallel Circuit- there are branches so currents are divided
LEDS-Light emitting diode
Diodes : A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance). It has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
Anode=+, Cathode=-
Breadboards
ATTENTION!!! Avoid removing or changing components o na breadboard whenever the board is powered you risk shocking or dying D:
Transistor
These are used to amplify or switch electronic signals (Digital switch)
Tutorials
Ohms Law
Photoresistor
Series and parallel circuits
Light emitting diode
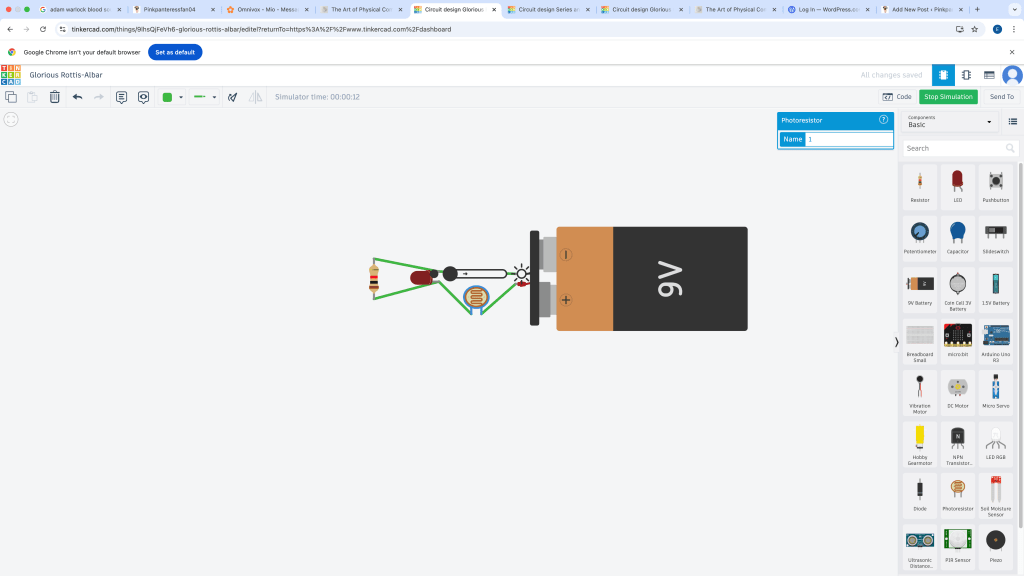
Putting the work to practice in real life

